Summary
AI agents pose an existential threat to online survey research (see Westwood, 2025). As generative AI advances, researchers face the critical challenge of distinguishing authentic human responses from sophisticated AI-generated data.
CloudResearch has developed the industry’s first comprehensive, platform-integrated solution for detecting and preventing AI agents from participating in online surveys. Together, our Engage survey platform and Connect participant marketplace provide a multi-layered detection system that combines behavioral analysis, machine learning, strategic interventions, and rigorous participant vetting.
In this white paper, we describe the current threat to survey research and report results from a controlled test of the Engage survey platform’s AI-detection features. The test was conducted with over 1,000 survey completions that included 500+ responses from advanced AI agents and 500+ responses from real, human participants. In the test, our system achieved a 100% success rate in detecting AI agents while maintaining a false positive rate of less than 1% for legitimate human responses. After reporting the results of the test, we discuss how CloudResearch will stay ahead of the threats to online research going forward.
The Challenge: An Accelerating Arms Race
AI agents threaten survey research in multiple ways. First, they can commit fraud at scale. Automated agents can complete hundreds or thousands of surveys simultaneously. Second, a global network of bad actors can use AI to help them complete surveys at scale. Third, advanced agents can attempt to replicate human behavioral patterns within surveys. As demonstrated by Westwood (2025), AI can adopt a human persona and generate responses throughout an entire survey that are consistent with that person (Westwood, 2025). This makes AI responses hard to detect.
In response to these threats, researchers must develop more sophisticated defenses. AI agents easily pass attention checks and rare event items that were designed to catch (and often still catch) people committing survey fraud or not paying attention (Westwood, 2025). Detecting and deterring AI agents is important because even a small percentage of AI-generated responses can compromise the validity of studies that rely on survey data, such as polling, social science research, medical research, market research and other forms of descriptive and experimental studies.
The Engage Platform: AI Detection From the Ground Up
Within the past few years, CloudResearch has created a survey platform called Engage. Engage is similar to Qualtrics, RedCap, Alchemer, and other platforms commonly used for surveys, experiments, and various forms of quantitative or mixed methods research. Unlike other platforms, however, Engage has been built with advanced generative AI. The AI allows researchers to conduct “conversational surveys,” that enable qualitative and mixed methods research to be done at scale. The AI can interview participants, follow up on closed ended questions, and analyze open ended data. In addition, Engage contains state of the art data quality protection, including AI agent detection, that other platforms lack.
Engage was designed with AI detection as a core feature. Within an Engage survey, every interaction between the participant and the device, indeed, every data point is captured with the explicit purpose of identifying anomalous behavior that may harm data quality.
In the screenshot below (Figure 1), for example, the red line tracks the movement of a participants’ mouse across the screen.
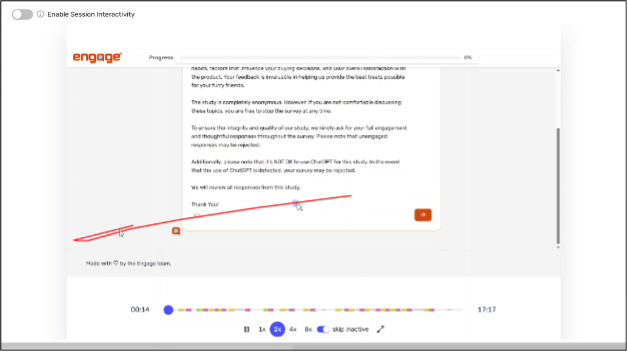
Figure 1. A session recording from Engage shows mouse tracking technology. Every participant survey is recorded and anomalous behaviors are flagged.
Every Engage survey is recorded, allowing researchers to see what happens on the participants’ device as the survey is completed. These session recordings also contain surreptitious measures designed to detect whether AI is being used to complete the survey. The result is a survey tool that captures a range of behaviors and device data that other survey platforms do not track, giving researchers an unprecedented look at participants as they complete the survey.
Engage’s Multi-Layered Detection Methodology
As mentioned above, every Engage survey is recorded to give researchers an unprecedented look at the participants completing their studies. At the same time, these recordings are a rich collection of participant responses and behaviors, already numbering in the millions, that CloudResearch can use to explore differences in human and bot behavior.
Some differences are obvious. For instance, mouse movements. Human mouse movements are rarely clean. Instead, they unfold in smooth but imperfect arcs. They often begin with an initial sweep toward the target followed by a series of subtle corrections as the hand, eye, and brain continuously recalibrate. This produces paths that gently curve, bend, and swerve, even when the intention is to move directly from point A to point B. Humans also tend to overshoot and loop back. Rather than stopping abruptly, the cursor may glide past the intended endpoint, slow down, and reverse direction in a small hook or spiral before settling.
In contrast, AI-generated mouse movements tend to be tidy and behaviorally hollow. They get to the right place, but they lack the process that characterizes human motion. The cursor may move in a near-perfect line or a smooth, idealized curve, as if pulled by an invisible ruler or spline. Even when curvature is added, it is usually too smooth and symmetrical. The path looks planned all at once, not continuously adjusted. These differences can be seen with the naked eye.
In studies conducted by our team, we have identified numerous behavioral signatures that distinguish machine responses from human responses. Internally, we call these signatures “AI smells.”
We use machine learning to examine differences in human data and machine generated data that is invisible to the naked eye. From millions of sessions, we have created “profiles” of participant behavior for humans and AI’s based on numerous “AI smell” signals. This allows us to find “AI smells” that are not visible to the naked eye.
In multiple recent studies, we have tested our ability to detect these “AI smells” in studies conducted with human and AI generated responses. Below is a summary of some AI-detection methods. This list is intentionally incomplete.
Behavioral Pattern Recognition: “AI Smells”
AI agents behave differently from humans in subtle but detectable ways. Some of these include:
Text Input Patterns
- AI agents often modify webpage content directly rather than simulating typing
- When AI agents do type, they exhibit unnatural cadence and patterns
- Typing speed, rhythm, and error correction differ fundamentally from human behavior
Navigation and Interaction
- Mouse movement patterns and trajectories
- Scrolling behaviors and timing
- Element interaction sequences
- Response timing distributions
Attention Patterns
- Time spent on different survey elements
- Reading speed versus content complexity
- Pattern of engagement with multimedia content
A Study Testing the “AI Smells” Within Engage
Study Description
To validate our detection capabilities against current-generation AI agents, we conducted a controlled study with 500+ survey completions by advanced AI agents and 500+ survey completions by human participants. The AI agents used multiple state-of-the-art AI models and frameworks. The human participants were recruited through standard online protocols.
Measures
The survey began with multiple demographic questions. These asked about things like age, gender, race, and ethnicity.
After the demographics, participants were presented with two pictures of people “eating fire.”
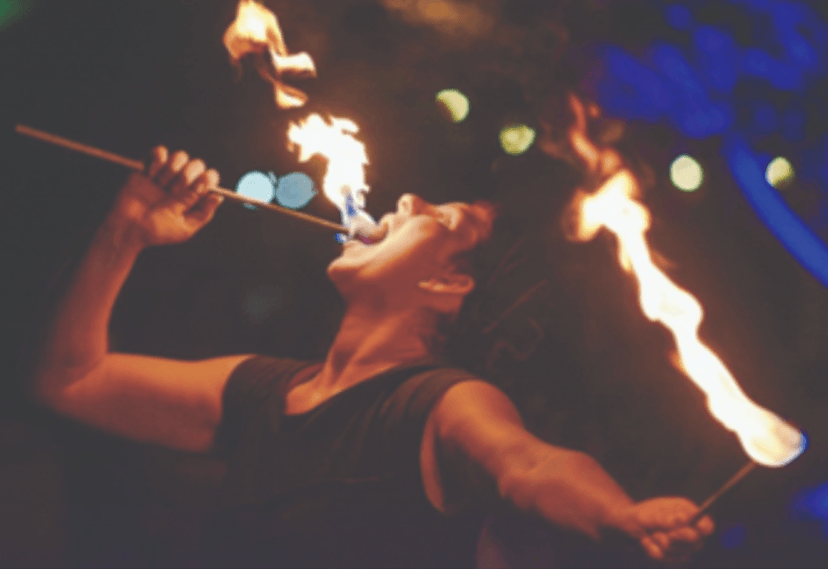
These pictures were of professional performers. Participants were asked to describe, in an open-ended text box, the feelings and associations each image brought to mind. After describing their associations, participants were asked what they call the job of the people in the images before being presented with a matrix question that measured perceptions of different terms related to fire eaters.
Following the question matrix, participants were reminded of the feelings and association they expressed earlier about fire eaters and they were asked to elaborate further on why they felt that way.
Finally, the survey ended with a series of three questions. The first asked how they felt about a brand using modern-day fire eaters in an ad; the second asked whether they were aware of a historical connection between the term fire eaters and slavery; and the third asked whether, after being informed about the historical connection, they still felt comfortable with a brand using modern day fire eaters in an ad. The study ended with a few more checks of attention.
Overall, the survey represents what is typical in market research product development. In fact, the survey came from a real study that CloudResearch conducted in collaboration with Kellogg’s and presented at a conference. The presentation can be viewed here for more context.
After all of the data were gathered, from humans and AIs, we blindly evaluated each response. That is, our detection systems operated without knowing which responses came from AI versus humans.
Statistical Analyses
To evaluate the effectiveness of the Engage AI detection system, we employed binary logistic regression to classify survey respondents as either human or AI agent. The dependent variable was respondent type (0 = human, 1 = AI agent), and the independent variables consisted of the behavioral indicators (“smells”) captured throughout the survey, including text input patterns, navigation behaviors, response timing distributions, and other metrics.
The sample comprised 1,000+ survey completions: approximately 500 from verified human participants and 500 from advanced AI agents operating across multiple state-of-the-art frameworks.
Model performance was assessed using standard classification metrics: detection rate (sensitivity), false positive rate (1 − specificity), and overall classification accuracy. Individual smell indicators were also evaluated independently to assess their relative contribution to detection (see Figure 2).
The integrated model achieved a 100% detection rate for AI agents with a false positive rate below 1% for human respondents, indicating strong discriminant validity across behavioral indicators.
Results
Our integrated detection system achieved:
- 100% detection rate for AI agent responses
- <1% false positive rate for human responses
- Real-time flagging during survey completion
- Zero false negatives across all tested AI frameworks
These results demonstrate that the current Engage system is highly effective against today’s AI agents, including those specifically designed to evade detection. The figure below shows detection rates across some of the “AI smells” we examined.
Test Success Detection Results by Bot Smell and Survey
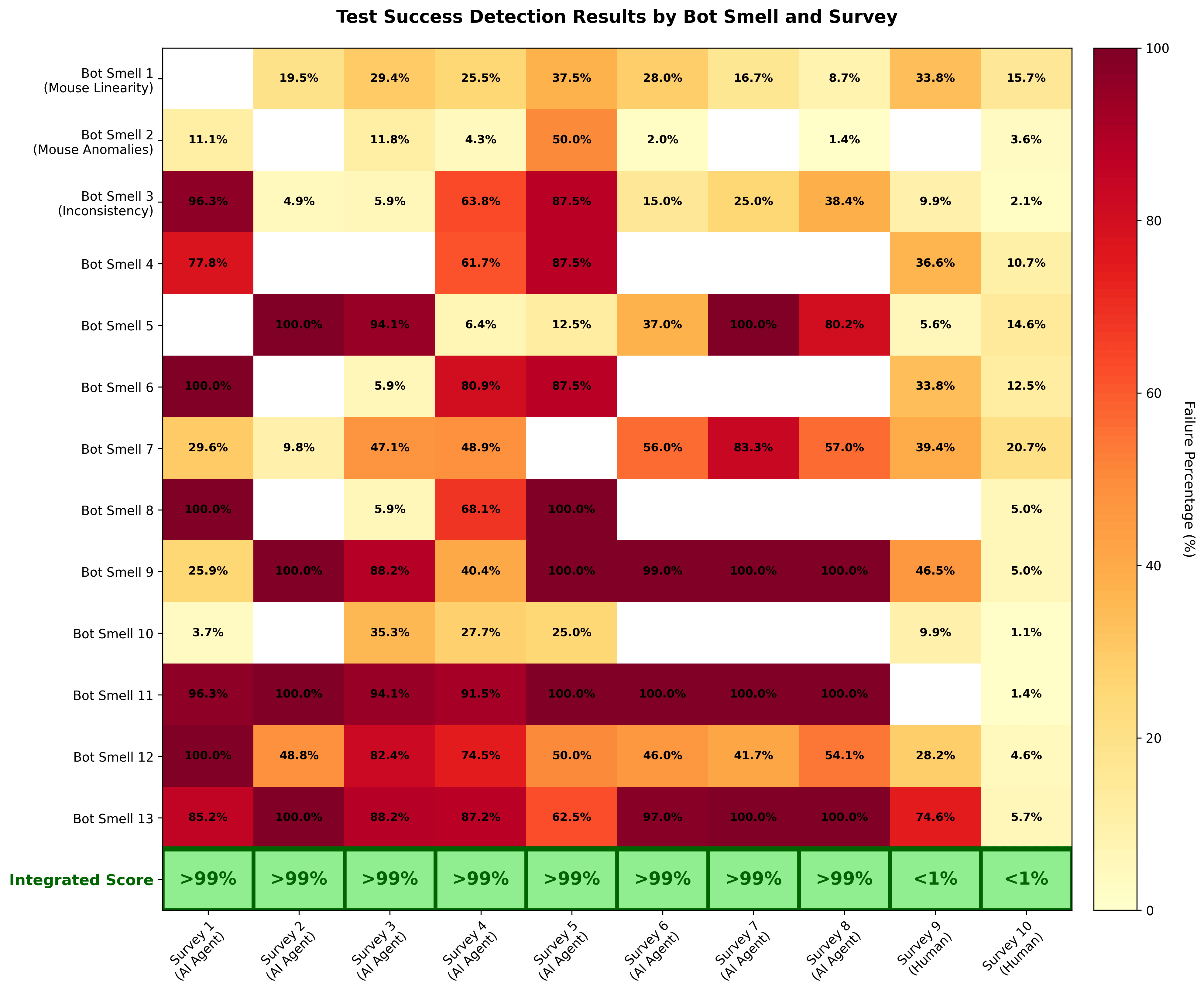
Figure 2. The percentage of participants flagged as bots based on each smell test. Multiple smell tests are combined with different weights into the integrated score.
Standard Detection Measures
While our analysis of “AI smells” identified many metrics that humans and AI’s vary on, our assessment of more traditional attention checks that are used to detect fraud and inattention showed little variability based on the source of the data. For example, when asked if they belong to the fictional LPAKE group, 98.6% of humans said no. Similarly, 96% of AI generated responses said ‘no.’
Another item asked participants if they were employed as a petroleum engineer. About one tenth of one percent of the US workforce . Human participants responded ‘no’ 99.4% of the time. AI generated responses said ‘no’ 98.2% of the time.
When instructed in a standard attention check item to select “somewhat agree,”, both AI (100%) and human (99.3) respondents selected the correct response.
The table below shows pass rates for AI agents and human participants across the four attention check questions included in the study. The overall pass rates were similar, showing that AI agents pass attention checks as well as humans.
| Number of Checks Passed | AI Agents | Humans |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 3.5 |
| 1 | 0 | 0.3 |
| 2 | 2.4 | 4.2 |
| 3 | 6 | 3.6 |
| 4 | 91.6 | 88.4 |
What CloudResearch is Doing to Detect Future Threats
We recognize there is no permanent “solution” to AI detection. The future contains many unknowns and AI is rapidly advancing. What works today may not work tomorrow. Nevertheless, we are confident about CloudResearch’s ability to stay in front of AI threats thanks to our machine learning process, our Red Team/Blue Team strategy, and the integration of Engage with Connect for mutually reinforcing feedback.
Machine Learning Approach
As mentioned above, CloudResearch employs advanced machine learning models to analyse how millions of humans behave within surveys. One reason our models are effective is because they have a lot of rich data to work with. CloudResearch conducts continuous research to measure and monitor data quality across the entire online ecosystem.
Red Team / Blue Team Framework
As part of our research and development process, CloudResearch maintains both offensive and defensive AI teams. We call these the Red team and Blue team.
Our red team continuously develops sophisticated AI agents designed to bypass our detection systems. This team uses state-of-the-art AI technologies to simulate advanced fraud attempts and is rewarded for breaking our defenses.
Our blue team, on the other hand, designs and implements protective barriers. The blue team is specifically designed to block red team agents and other other AI agents designed to complete online surveys. The adversarial nature of these teams ensures that we are always testing our systems against the most sophisticated possible attacks, not just those we have encountered in the past.
Cross Platform Integration: Participant Vetting on Connect
Over the course of the year, tens of millions of online studies are completed on Connect, CloudResearch’s online panel. These participants go through a rigorous vetting process with multiple layers of verification that include:
- Government ID verification at registration
- Continuous behavioral monitoring across all survey participation
- Strong disincentive structure: Participants caught using AI are permanently banned, creating substantial deterrence
- Multi-factor authentication and device fingerprinting
- Longitudinal analysis of behavioral consistency
These vetting procedures create a trusted participant pool for research and where we can be confident participants will provide quality, human data. Because CloudResearch continuously monitors Connect participants in Engage surveys, we also get data to use in our machine learning models and other research aimed at identifying AI agents. In other words, we use Engage to vet Connect participants and then use the data from those participants to continuously improve Engage’s AI detection tools. This mutually reinforcing system created a positive feedback loop that improves data quality.
Conclusion
The threat of AI agents in survey research is real, accelerating, and requires sophisticated, multi-layered solutions. CloudResearch’s approach combines architectural foresight, behavioral science expertise, machine learning sophistication, adversarial testing, and rigorous participant vetting to deliver the industry’s most comprehensive response to this challenge.
CloudResearch’s validated 100% detection rate against current AI agents, combined with a commitment to continuous evolution, positions CloudResearch as the trusted partner for researchers who require authentic human intelligence in their data.
The future of AI capabilities remains uncertain, but our commitment to staying ahead of emerging threats is absolute. AI-detection was built into the foundation of the Engage because we knew this day would come.
The Team Behind the Technology
CloudResearch employs a large team of PhD-level researchers, including behavioral scientists, data scientists, and machine learning experts, dedicated to the AI detection challenge. This interdisciplinary team brings together expertise in human behavior and decision-making; deep learning and machine learning capabilities; survey methods and research design; and website technology and fraud detection.
Watch our MRII Webinar
Key Takeaways
Traditional Detection is Obsolete
- Standard attention checks, logic puzzles, and “reverse shibboleths” are no longer effective—AI agents now pass them at a 99.8% rate.
The Economics Are Shifting Rapidly
- While human fraud is currently more cost-effective than autonomous agents, this barrier is temporary—AI-driven fraud will soon become scalable and economically viable.
Shift from “What” to “How”
- To distinguish humans from AI, move beyond analyzing what participants answer—focus on how they answer: mouse trajectories, keystroke dynamics, and velocity profiles.
Event Streaming Achieves >99% Accuracy
- In blind validation testing against sophisticated AI agents, Engage’s Sentry system achieved an integrated detection score of >99% with a false positive rate below 1%.
The “Cat and Mouse” Requires Evolution
- There is no permanent solution to AI fraud—defense requires a Red Team / Blue Team approach where new attacks constantly test and refine detection algorithms.
Deterrence is Key to Prevention
- Combining real-time behavioral flagging with verified participant pools and permanent ban policies creates a risk-reward structure that makes AI-based fraud economically unviable.
About CloudResearch
CloudResearch provides researchers with access to diverse, high-quality participants through our Connect marketplace, sophisticated fraud detection through our Sentry platform, and advanced survey capabilities through our Engage platform. Founded by researchers for researchers, we’re committed to maintaining the integrity and quality of online research in an AI-augmented world.
For more information:
- Engage Platform: engage.cloudresearch.com
- Connect Marketplace: connect.cloudresearch.com
- Contact: support@cloudresearch.com
This white paper represents current capabilities as of December 2025. Given the rapid pace of AI development, CloudResearch continuously updates its detection methodologies and will provide regular updates on our evolving approach.